使用 C++ 读取简单的 24、32 位 BMP 图像
BMP 是 Windows 下常见的一种位图格式。之所以我们选择直接读取 BMP 格式(即不使用其他的库)而非 JPG、PNG 等其他图像格式,是因为:
- BMP 的文档是公开的。没有版权、专利问题。
- 运用较广泛,常见。
- 结构相对简单,一般来讲没有压缩,代码容易写。
接下来,我将尝试用最简单的方式来介绍 BMP 格式的结构,并且尽可能让之后出现的代码不依赖于具体的操作系统平台与特定的编译器实现。建议备一个十六进制查看器以方便理解。
(下文可能会有错误,并且不会处理「特殊的」BMP 文件。等我高考完之后如果还有兴趣,可能会再去做其他情况下的 BMP 文件读取。)
文件头 1:BITMAPFILEHEADER
BITMAPFILEHEADER 有四小块。如下表:
| 名称 | 大小(字节) | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
bfType |
2 | Windows 格式的 BMP 文件为「BM」。 |
bfSize |
4 | BMP 文件的大小。 |
bfReserved1 |
2 | 保留值。 |
bfReserved2 |
2 | 保留值。 |
bfOffBits |
4 | 位图像素内容的偏移量(起始地址)。 |
可能没有什么特别的地方,bfType 中检查是不是 BM 就行了,OS/2 有其他类型的 BMP 格式,可是也不想想它死了多少年了……
注意,文件头中的所有数据均以小端序存放。(简单而很不严谨地说,就是字节倒着读)
文件头 2:BITMAPINFOHEADER
其实在这个位置是有其他版本的不同的文件头的,但是一般的 BMP 文件都是 BITMAPINFOHEADER。
它有十一小块,如下表:
| 名称 | 大小(字节) | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
biSize |
4 | 此文件头(BITMAPINFOHEADER)的大小。 |
biWidth |
4 | 图像的宽度,以像素为单位。 |
biHeight |
4 | 图像的高度,以像素为单位。 |
biPlanes |
2 | 图像的色彩平面,正常情况下均为 1。 |
biBitCount |
2 | 每个像素的位数。 |
biCompression |
4 | BMP 文件的压缩种类,0 为无压缩。 |
biSizeImage |
4 | 位图像素内容的大小,无压缩时可以填 0。 |
biXPelsPerMeter |
4 | 图像横向每米存放的像素。 |
biYPelsPerMeter |
4 | 图像纵向每米存放的像素。 |
biClrUsed |
4 | 图像使用的色彩数,可以为 0。 |
biClrImportant |
4 | 图像使用的「重要」的色彩数,0 时均重要。 |
因为我们不想写解压算法,所以需要保证处理的 BMP 文件的 biCompression 为 0。我们之后也不想处理调色板(Color Table, Palette),而是直接读取像素内容,所以需要保证 biBitCount 为 24 或者 32(即 24 或 32 位的位图),因为它们一般是不含调色板的。
注意,图像的高度可以为负。负数值表示接下来的像素内容将从左上角从左到右、从上到下读取;而正数值表示接下来的像素内容将从右下角从左到右、从下到上读取。必要的时候请记得取绝对值。
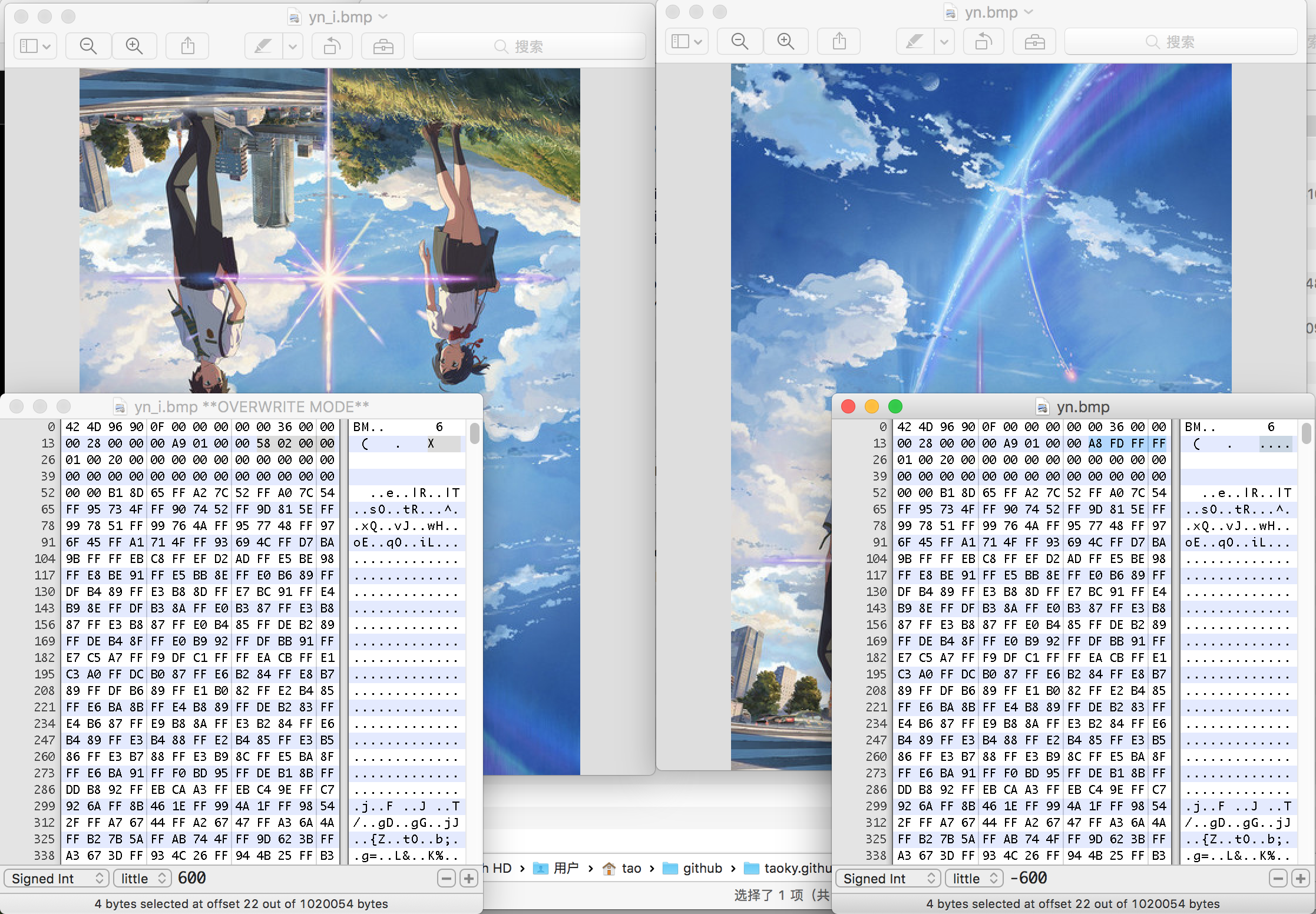
(对 biHeight 取相反数后的结果,改了四个字节,图像就反过来了~)
像素内容
接下来就是我们期待的位图像素内容了。我们之前说过忽略了调色板等其他的东西,所以在 BITMAPINFOHEADER 之后便直接是像素内容了。
标题中只写了 24 位和 32 位的图像,所以更低的位数不考虑。(毕竟你现在,除了在 gif 动图之外,还能见到 8 位色的图像吗?)
在 24 位(3 字节)的位图中,每个像素按顺序由三部分组成:蓝色值、绿色值、红色值。32 位(4 字节)的图像添加了 Alpha 透明度部分,在红色值后添加了一字节的 Alpha 值(不透明的 32 位 BMP 图像,每个像素的 Alpha 值字节十六进制均为 FF)。
然后我们只需要一个一个读就行了吗?
当然不是。还有一个特别的注意点:图像每行的字节大小都必须是 4 字节的倍数。不足的需要补齐。当然很明显的是,32 位的 BMP 就不需要考虑这一点了。
一切准备好了。所以,让我们开干吧。
具体实现
(这个实现比较草率,因为我确实时间不多了。)
首先把两个文件头,加上表示像素的结构,包在 struct 里面:
struct BITMAPFILEHEADER
{
char bfType[2]; // must be "BM"
char bfSize[4]; // the size of the bmp file
char bfReserved1[2];
char bfReserved2[2];
char bfOffBits[4]; // the offset to the bitmap data
} FileHeader;
struct BITMAPINFOHEADER
{
char biSize[4]; // the size of BITMAPINFOHEADER
char biWidth[4]; // width (pixels)
char biHeight[4]; // height (pixels)
char biPlanes[2]; // color planes
char biBitCount[2]; // bits per pixel
char biCompression[4]; // type of compression (0 is no compression)
char biSizeImage[4]; // the origin size of the bitmap data (before compression)
char biXPelsPerMeter[4]; // horizontal pixels per meter
char biYPelsPerMeter[4]; // vertical pixels per meter
char biClrUsed[4]; // the number of colors used
char biClrImportant[4]; // "important" colors, usually 0
} InfoHeader;
struct Pixel
{
unsigned char b;
unsigned char g;
unsigned char r;
} p;
为了能够把小端序转换成整型变量,我们还需要一个小函数:
inline int ToHumanRead(char *str, int size = 4)
{
// Convert to Big Endian
long l = 0;
memcpy(&l, str, size);
return (signed int)l;
}
在主函数部分,我们先读取文件,然后进行进一步操作:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
cout << "Parameters Error." << endl;
cout << "Use: " << argv[0] << " xxxx.bmp" << endl;
return 1;
}
bmpfile.open(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary); // open the file
if (bmpfile.is_open())
{
bmpfile.read((char *)&FileHeader, sizeof(FileHeader)); // Read BITMAPFILEHEADER
if (strncmp(FileHeader.bfType, "BM", 2) != 0) // Judge whether a BMP.
{
cout << "Not a BMP File, or an Unsupported OS/2 BMP File." << endl;
return 1;
}
bmpfile.read((char *)&InfoHeader, sizeof(InfoHeader)); // Read BITMAPINFOHEADER
/* Information Output */
Output_FileHeader();
Output_InfoHeader();
/* Output End */
vector <Pixel> *vec = ReadBitmap(); // Read the data
int x, y;
while (cin >> x >> y)
{
if (x == -1) break;
PrintLocation(x, y, vec);
}
// Close file and delete vec
bmpfile.close();
delete [] vec;
}
else
{
cout << "Open File Error." << endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
其中的 vector 是用来储存像素内容的,Output 部分输出 BMP 文件头内容,使用 ReadBitmap() 读入后等待用户输入坐标,显示对应像素的 RGB 值。
Output 部分:
void Output_FileHeader()
{
cout << "File Size (BITMAPFILEHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(FileHeader.bfSize) << endl;
cout << "Reserved 1 (usually 0, BITMAPFILEHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(FileHeader.bfReserved1, 2) << endl;
cout << "Reserved 2 (usually 0, BITMAPFILEHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(FileHeader.bfReserved2, 2) << endl;
cout << "Bitmap Data Offset (BITMAPFILEHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(FileHeader.bfOffBits) << endl;
}
void Output_InfoHeader()
{
cout << "BITMAPINFOHEADER Size: " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biSize) << endl;
cout << "Width (BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biWidth) << endl;
cout << "Height (BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biHeight) << endl;
cout << "Number of Color Planes (BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biPlanes, 2) << endl;
cout << "Number of Bits per Pixel (BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biBitCount) << endl;
cout << "Compression Type (0 is none, BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biCompression) << endl;
cout << "Original Size of Bitmap (0 usually if no compression, BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biSizeImage) << endl;
cout << "Number of Horizontal Pixels per Meter (0 usually, BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biXPelsPerMeter) << endl;
cout << "Number of Vertical Pixels per Meter (0 usually, BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biYPelsPerMeter) << endl;
cout << "Number of Color Used (0 sometimes, BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biClrUsed) << endl;
cout << "Number of Important Color (0 means all is important, BITMAPINFOHEADER): " << ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biClrImportant) << endl;
}
写得比较草率。将文件头的内容全部输出。
读取部分:
void drop_alpha()
{
if (ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biBitCount) == 32)
{
unsigned char null;
bmpfile.read((char *)&null, sizeof(null));
}
}
vector <Pixel> * ReadBitmap()
{
int offset = 0;
int height = ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biHeight);
int width = ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biWidth);
int linebyte = width * ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biBitCount) / 8;
offset = linebyte % 4;
if (offset != 0) offset = 4 - offset; // "linebyte" should be the multiple of 4
// cout << "Bytes per line: " << linebyte << endl;
cout << "Offset: " << offset << endl;
vector <Pixel> *vec = new vector <Pixel> [abs(height)];
// Height could be a negative number.
bool isBottom = false;
if (ToHumanRead(InfoHeader.biHeight) > 0) // read from bottom
{
isBottom = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < abs(height); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
bmpfile.read((char *)&p, sizeof(p));
if (!isBottom) vec[i].push_back(p);
else vec[height - i - 1].push_back(p);
drop_alpha();
}
for (int j = 0; j < offset; j++)
{
unsigned char null;
bmpfile.read((char *)&null, sizeof(null));
}
}
return vec;
}
drop_alpha() 是为了把 32 位位图中的 Alpha 信息丢掉,方便处理,当然你也可以把它们留着……ReadBitmap() 部分先计算 offset(每行需要补齐的字节),再根据高度的正负值分类读取数据。
最后一个部分,输出 RGB 值:
void PrintLocation(int x, int y, vector <Pixel> * vec)
{
cout << (int)vec[x][y].r << " " << (int)vec[x][y].g << " " << (int)vec[x][y].b << endl;
}
完整的代码在此。
Comments